University of Redlands Emergency Alert System
Alert Received: . For more information, visit: https://www.redlands.edu/alert/
University of Redlands
- Home
- Trees
- Species Accounts
- Coast Live Oak
Common Name: Coast Live Oak; California Live Oak, Encina
Scientific Name: Quercus agrifolia
Family: Fagaceae
Identification:
Habit:
-Slow-growing evergreen tree (typical age in cultivation ranges from 40-110 years)
-At maturity, height range is 25-80 ft. (8-25 m, in cultivation)
-At maturity, width range is 15-35 ft. (5-11 m, in cultivation)
-Branches tend to extend almost to ground level.
-Has round to broad and dense crown.
-Commonly has a densely branched trunk.

Leaves:
-Alternate leaf pattern
-Oval or rounded, convex (cupped downward) leaves
-Can grow up to 2 ½ in. (7 cm) long
-Short-stalked
-Hard and leathery texture
-Spine-tipped edges
-Smooth and shiny green on top of leaf
-Duller green and fuzz present on bottom of leaf.

Twigs and Bark:
-Twig commonly has a slender width.
-Twig has clustered end buds.
-Reddish brown twig color.
-Broad, rounded twig tips (buds).
-Bark is gray-brown when young and black and brown striped when mature.
-Bark becomes darker as it matures.
-Bark is smooth and develops light gray ridges as it matures.


Flowers and Fruits:
-Flowers have both male and female reproductive organs (monoecious).
-Male organs in 2-4 in. (5-10 cm) long, yellow-green drooping part of flower (catkin).
-Female organs found in red-green spike at leaf axis.
 -Fruit produced is a light-brown acorn that are about ¼ enclosed in the cup.
-Fruit produced is a light-brown acorn that are about ¼ enclosed in the cup.
-Thin cone-shape with an average length of 1-1 ½ in. (2.5-4 cm)
-Takes almost a year to mature (usually ripen during early fall).


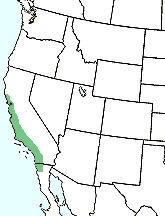
Where it’s from:
Native range:
-Coastal California and Mexican native species
-Currently most commonly grows west of central California valleys.
-Furthest northern grows in Mendocino County, California.
-Furthest southern grows in northern Baja California, Mexico.
-Tree often found in valleys and near streams.
-Thrives in USDA Hardiness zones of 8-11 (minimum winter temp. of 10°F (-12°C))

Ecological notes:
-Coast Live Oak uses a deep taproot system that is commonly partnered with water-uptake-aiding soil fungi (mycorrhizae).
-Most acorns are dropped in fall, but some are dropped in spring to help avoid consumption by birds and squirrels.
-Acorns usually germinate 15-50 days after falling (no dormancy requirement).
-Susceptible to Sudden Oak Death, a fungal disease.
What we use it for
-The cooked seed is considered a staple food source used by Native American Indian tribes. (dried or ground into powder to thicken stews)
-Galls on tree (abnormal growths sometimes found on tree; caused by larvae of insects) are very astringent (drying), and can be used to help treat hemorrhages and dysentery.
-Mulch produced from leaves helps repel slugs from soil.
-Buttons can be made from seed cups.
 -catkin gall
-catkin gall
References
Image resources
Biographer:

Donald Johnson ‘21, FYS 20: Plants in Our World, Fall 2017.