University of Redlands Emergency Alert System
Alert Received: . For more information, visit: https://www.redlands.edu/alert/
University of Redlands
- Home
- Trees
- Species Accounts
- Silver Maple
Common Name: Silver Maple; Swamp Maple; Water Maple; Silverleaf Maple; White Maple; Soft Maple
Scientific Name: Acer saccharinum
Family: Sapindaceae (Soapberry Family)
Identification:
Habit: The Silver Maple Tree is one of the most common trees in North America. The tallest trees range from 50-70 feet (15.24-21.34 meters) tall at their mature height and 30-50 feet (9.14-15.24 meters) wide (Morton 2019). The Silver Maple is known for its fast-growing, yet weak-wooded trunk. It has a short stout trunk and a very wide crown, which is irregularly shaped. Its branches are slender and droop, but turn upwards at the tips (Britannica 2019).
 Figure 1. Silver Maple Tree.1
Figure 1. Silver Maple Tree.1
Leaves: The leaves are 8-15cm long (Nesom 2000). They are deeply cut and have five lobes. They are light green on top, yet silvery below (Britannica 2019). They are also star-shaped and tend to fall off at maturity (Gilman 1993).
 Figure 2. Silver Maple Tree Leaves.2
Figure 2. Silver Maple Tree Leaves.2
Twigs & Bark: The bark contains no thorns and the twigs have a slightly unpleasant odor when you crush them (Nesom 2000). The bark is gray and thin and is very easy to break off. The young bark is smooth, but as the tree ages, it becomes flakier (Britannica 2019). Therefore, bark requires maintenance under the tree to remove the flakes from under the tree. The roots are shallow in the ground and will lift sidewalks and interfere with mowing (Gilman 1993).
 Figure 3. Silver Maple Tree Twigs.3
Figure 3. Silver Maple Tree Twigs.3
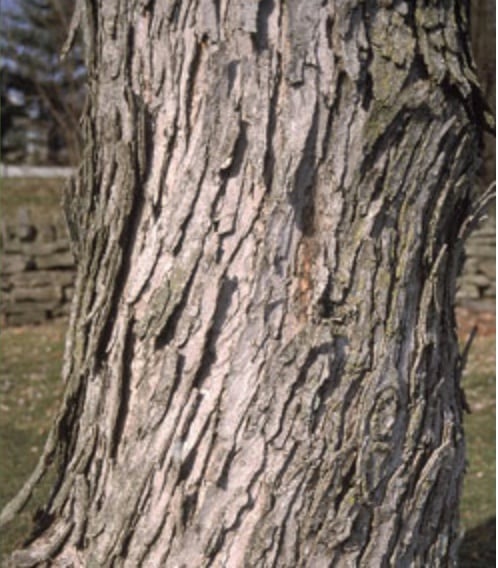 Figure 4. Silver Maple Tree Bark.4
Figure 4. Silver Maple Tree Bark.4
Flowers & Fruits: The paired, winged fruits are the largest of all the maple trees (Britannica 2019). Green flowers appear along the shoots before the leaves unfurl in springtime. The fruit is unappealing to wildlife and is also a bit garish (Gilman 1993). The tree has red flowers during the springtime. Individual trees commonly have all-male (fascicled) or all-female (drooping racemes) flowers. All flowers on one tree occur at the same time. They are a green or yellowish color coming from red buds about 6mm in length (Nesom 2000).
 Figure 5. Silver Maple Tree Fruit.5
Figure 5. Silver Maple Tree Fruit.5
 Figure 6. Silver Maple Tree Fruit.6
Figure 6. Silver Maple Tree Fruit.6
Where it’s from:
Native Range: Silver Maples are mainly found in eastern North America. They can also be found immediately adjacent to Canada, except along major portions of the Gulf and Atlantic coastal plains (Nesom, 2000). Its abundance in its natural habitat has decreased due to deforestation but has increased in urban areas because of people planting them for shade. It is mainly found in wetter soil. It can be found on stream banks, flood plains, and stream edges. They can be found in altitudes ranging from 100-2000 feet (30.48-609.6 meters) (Nesom, 2000). Its shade tolerance is moderate to poor. They can withstand many different environmental stressors as well such as flooding. They tend to grow very fast, but do not compete well with other species. It can tolerate its trunk being under a few feet of rain for a few weeks as well.
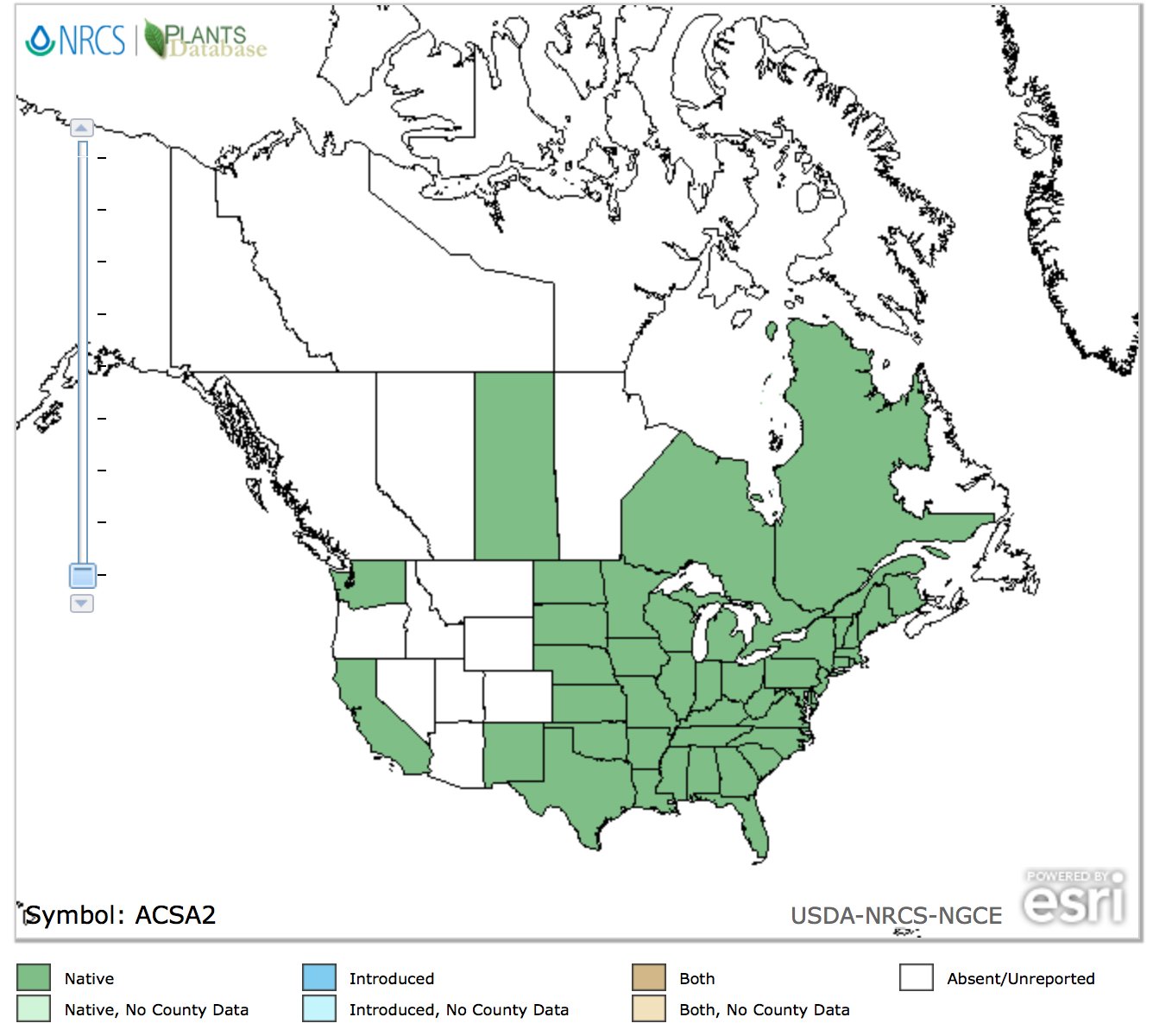 Figure 7. Native Range Map of Silver Maple Tree.7
Figure 7. Native Range Map of Silver Maple Tree.7
Ecological Notes: The many seeds that the Silver Maple Tree produces are a food source to various different birds, such as grosbeaks, finches, wild turkey, ducks, and mammals like squirrels and chipmunks (Nesom, 2000). The buds are important for squirrels especially when winter comes around and they have very scarce resources for food. The tree's bark is also food for beavers and the foliage is sometimes consumed by rabbits. Not only is the tree used for food, but it can also be used as protection for smaller animals because its droopiness creates shelters (Nesom, 2000). The tree is pollinated through wind dispersion. Some pests of the Silver Maple tree are the leaf stalk borer and petiole-borer. Both of these insects go into the leaf stalk and shrivel it, turning it black and making the leaf fall off (Gilman, 1993). Scale insects are also a problem for maples and the most common is the Cottony Maple Scale. This insect creates a cottony mass on the bottoms of branches. A Crimson Erineum Mite can also be found in maples and creates patches under leaves that are red and fuzzy (Gilman, 1993). A disease that the Silver Maple can get is anthracnose. This disease causes light brown areas on leaves that look like they are scorched. Another disease is verticillium wilt. This causes branches to wilt and die. If it is too severe, the tree cannot be saved (Gilman, 1993).
What we use it for:
The Silver Maple tree used to be planted in many urban areas as decoration, but that has since slowed down since people were unhappy with how much debris fell off the tree due to its brittle bark. The Silver Maple tree can grow very fast and used to be planted for “instant shade.” Its roots also grow very shallow to the ground, so it can ruin backyards, so that is another reason as to why people have slowed down planting them in their yards. The tree can also be planted as vegetative rehabilitation for surface-mined lands (Nesom, 2000). Its sap can also be used to make syrup, but it is the worst maple tree to use for syrup as its sap is very light and has very low amounts of sugar in it. Although it is not the best syrup, it can be used as a good cough syrup. The wood is brittle, but is hard as well and can be used to make furniture, cabinetry, flooring, paneling, musical instruments, wagons, boxes, and rails (Nesom, 2000). It can also be chopped down for lumber and old heartwood has a swirl pattern of a “bird’s eye maple.” Many people do still use this tree for landscaping projects even though it creates much debris.
References:
Photo References:
Biographers: Jake Stewart & Joseph Reyes ‘21, BIOL 238: Evolution, Ecology, & Behavior, Spring 2019