University of Redlands Emergency Alert System
Alert Received: . For more information, visit: https://www.redlands.edu/alert/
University of Redlands
- Home
- Trees
- Species Accounts
- Camphor Tree
Common Name: Camphor Tree
Scientific Name: Cinnamomum camphora
Family: Lauraceae
Identification
Habit: The camphor tree grows up to about 50-60 feet (15-18 m) tall and holds an umbrella shape that has a width up to 50 feet (15 m).
 Leaves: The leaves are a glossy light green and have a pointed oval-like shape with three main veins. They produce a strong odor of camphor when crushed. The tree may be evergreen in mild climates.
Leaves: The leaves are a glossy light green and have a pointed oval-like shape with three main veins. They produce a strong odor of camphor when crushed. The tree may be evergreen in mild climates.
 Bark: The color of the bark varies, and can be anywhere from a dark gray to a red-brown and has a very rough texture.
Bark: The color of the bark varies, and can be anywhere from a dark gray to a red-brown and has a very rough texture.
Flowers & Fruits: The tree produces clusters of small, off-white flowers in the spring which develop into a 3/16 inch (1/2 cm) round, black fruit called a drupe.

 Top: Camphor flowers in the spring, Bottom: Black drupes
Top: Camphor flowers in the spring, Bottom: Black drupes
Where it’s from
Native Range: The camphor tree is native to the tropical parts of Eastern Asia (the sub-tropics), but has adapted to dry soils and is currently found on most continents in both dry and humid climates. It grows best in sandy soils with a pH range of 4.3-4.8.
 http://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Cinnamomum+camphora&guide=Trees
http://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Cinnamomum+camphora&guide=Trees
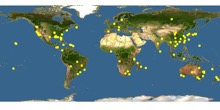
Ecological notes: The flowers produced by the camphor tree are hermaphroditic, meaning that every flower contains a male and female part making it easier to reproduce. The tree relies on birds and other animals eating the black drupes for seed dispersal. Because of the ability to adapt drastically and the ease of reproduction, the tree is considered invasive. In the US, the camphor tree is found in California and southern states. The Camphor is considered invasive on all continents, as seen on the map above.
What we use it for
Historically, the camphor tree has been used in paint, fragrance, and soaps. It is used by extraction of the oils. Three different kinds of oils are taken out in this process, two being toxic. The non-toxic oil has a whitish color and has been used as medicine for pain, hysteria, fainting, heart problems and respiratory issues. Currently, the white oil is used in cleaning supplies. The tree itself is valued for providing shade.
References
Biographer

Chloe Nicolet ’21, FYS: Plants in Our World, Fall 2017