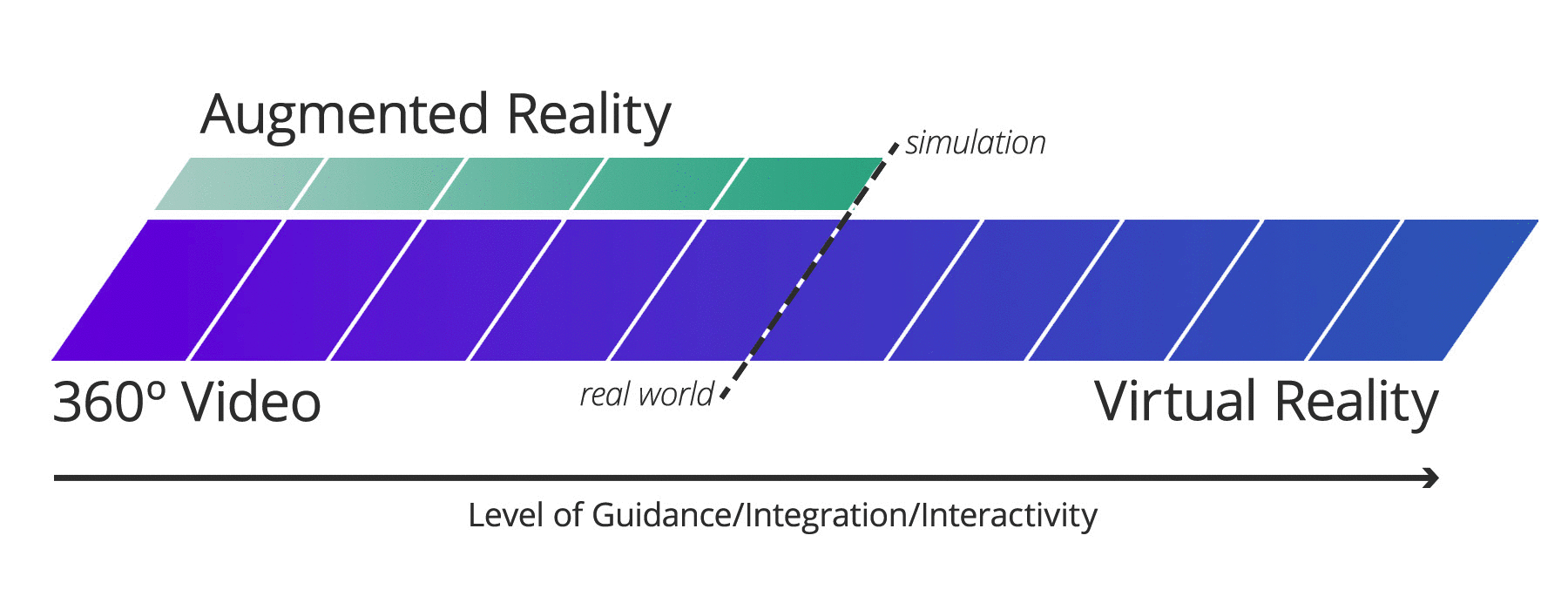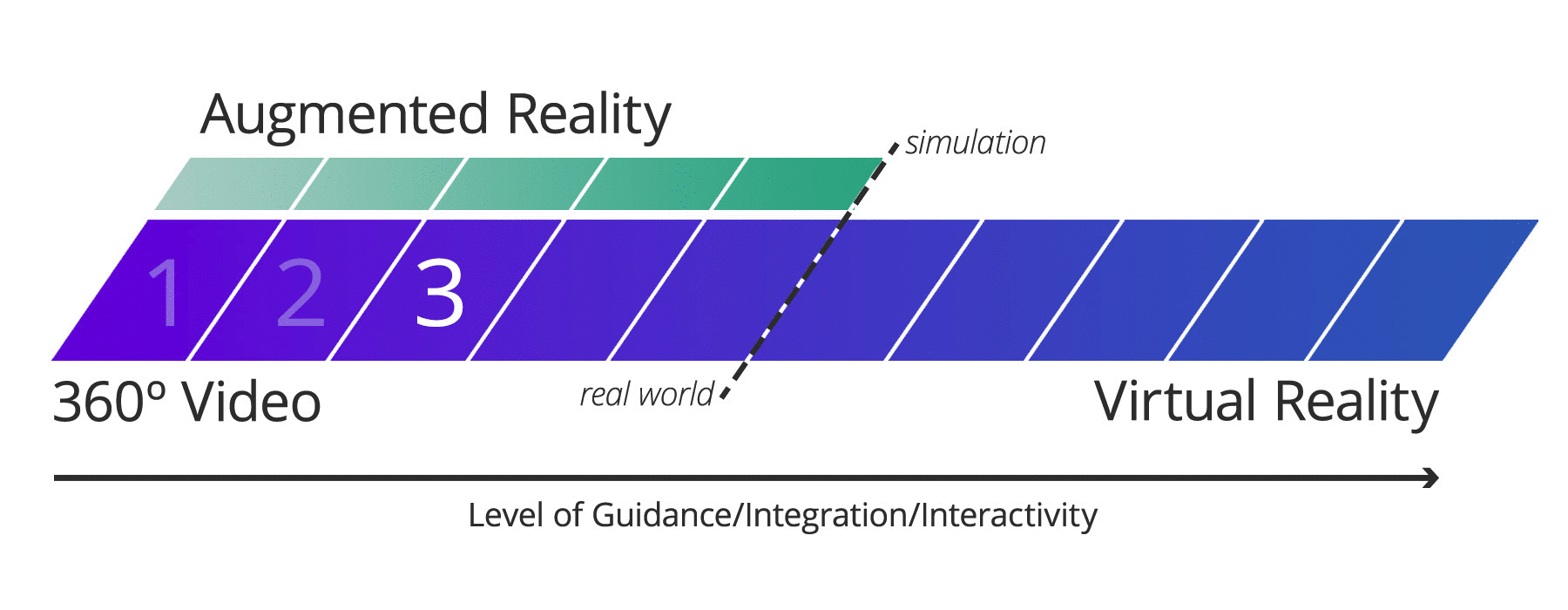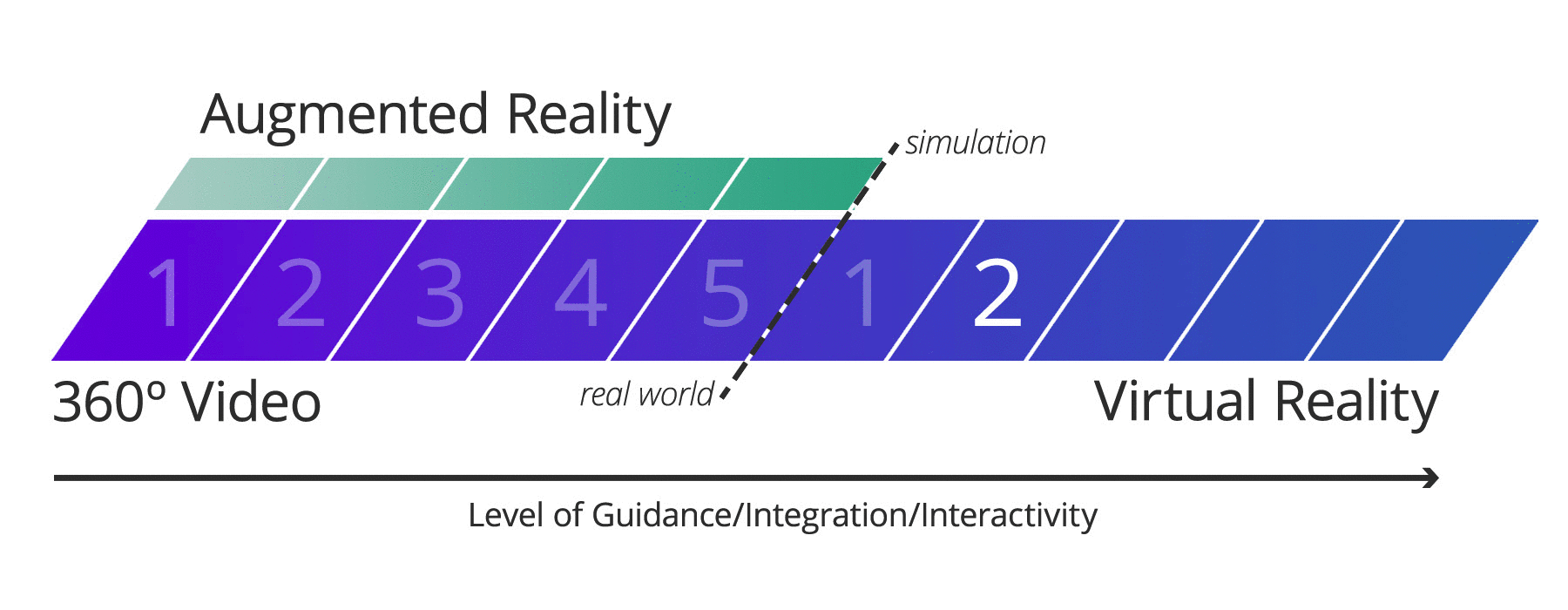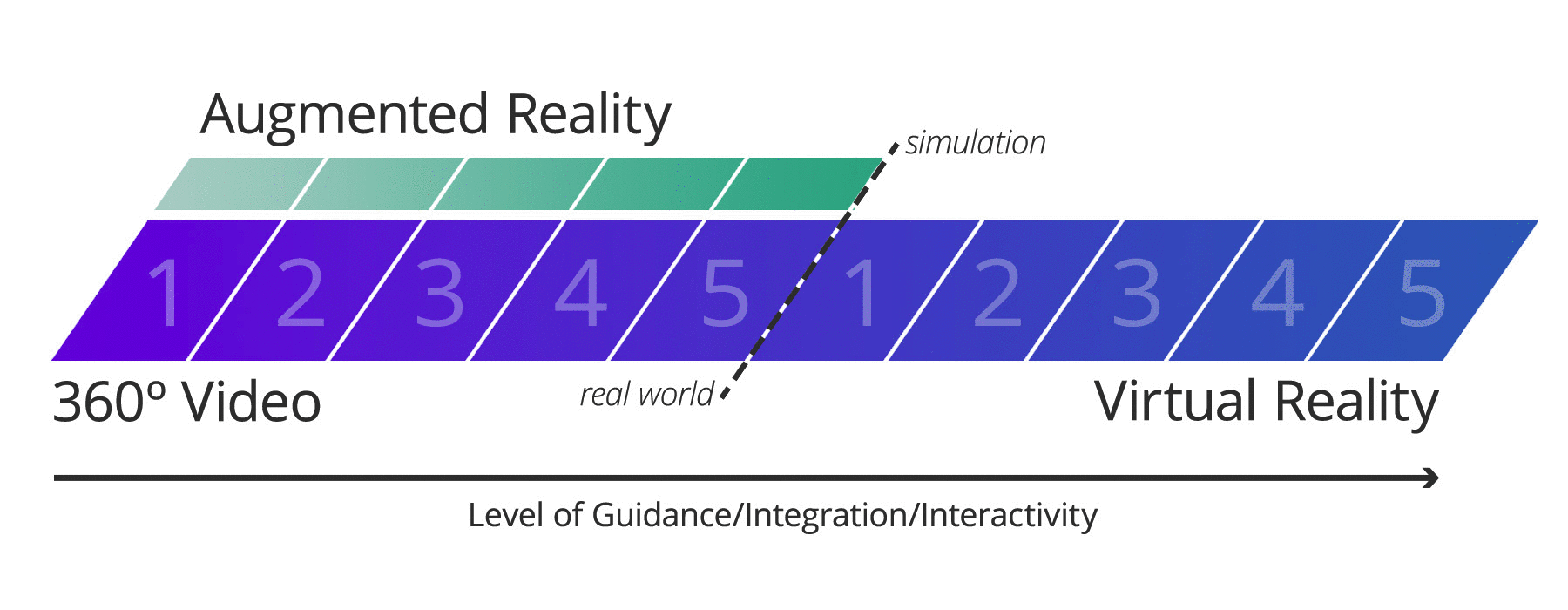
The viewer can enter a wholly created world through Virtual Reality (VR). This world may or may not be based on real-life experiences. In a simple VR experience, the viewer is placed inside a constructed space as a passive observer. On the other hand, an advanced VR experience allows the viewer to interact with and manipulate the environment around them, including building new items in 3D space, moving objects, talking with simulated characters, and more.
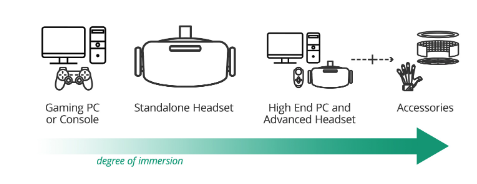
Most VR experiences are designed like computer games and can be loaded on a gaming PC or console, where the viewer would use a keyboard, mouse/trackpad, or a handheld controller to manipulate the simulated space. However, the audio and video quality may vary based on the device and its accessories.
A standalone headset can also be used to view VR content. The viewer can change their vantage point by moving their head, and basic interaction is navigated with a handheld controller. However, the headset's self-contained nature means that it does not provide motion tracking, and A/V quality is limited by the headset's specifications.
By using a high-end PC and an advanced headset, the viewer can experience far higher quality audio and video, and also motion tracking within the simulated environment through included accessories. However, the amount of physical space available and tactile/haptic feedback when interacting with objects using a handheld controller are constraints.
Adding high-end accessories to a PC and advanced headset can significantly increase the viewer's immersion. For example, haptic feedback gloves and other clothing can allow the viewer to feel objects and actions within the experience. VR platforms with moving floors or other dedicated spaces also allow the viewer to roam freely in-world.